-
Named a Leader in Fourth-Party Logistics
-
Shaping the future of supply chain
-
The mystery of silos
-
Supply chain orchestration
-
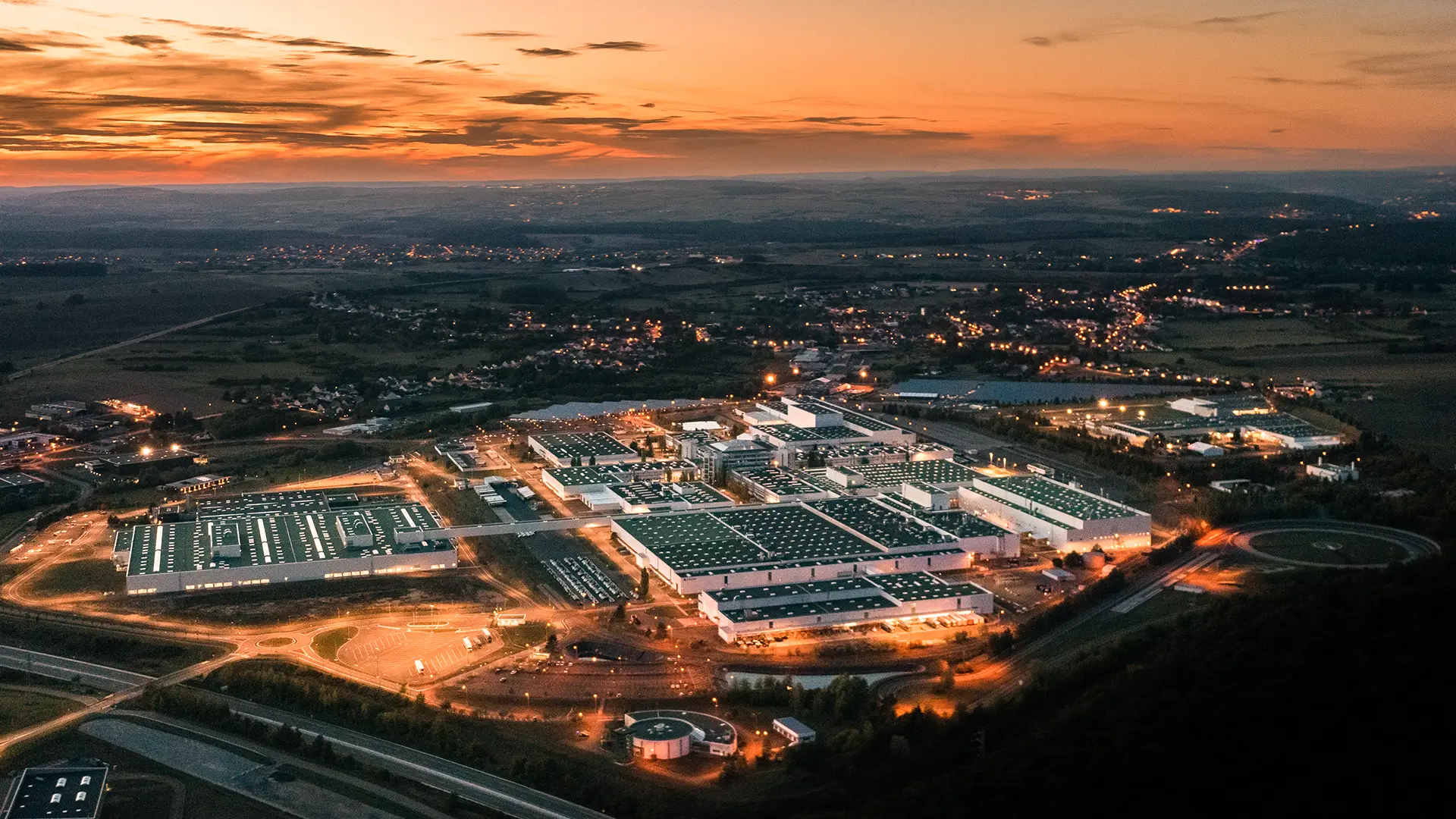
Selected success stories
ExploreTrusted by industry leaders
As an innovative partner, we collaborate with our customers to develop solutions for the future.
Contact us




















































































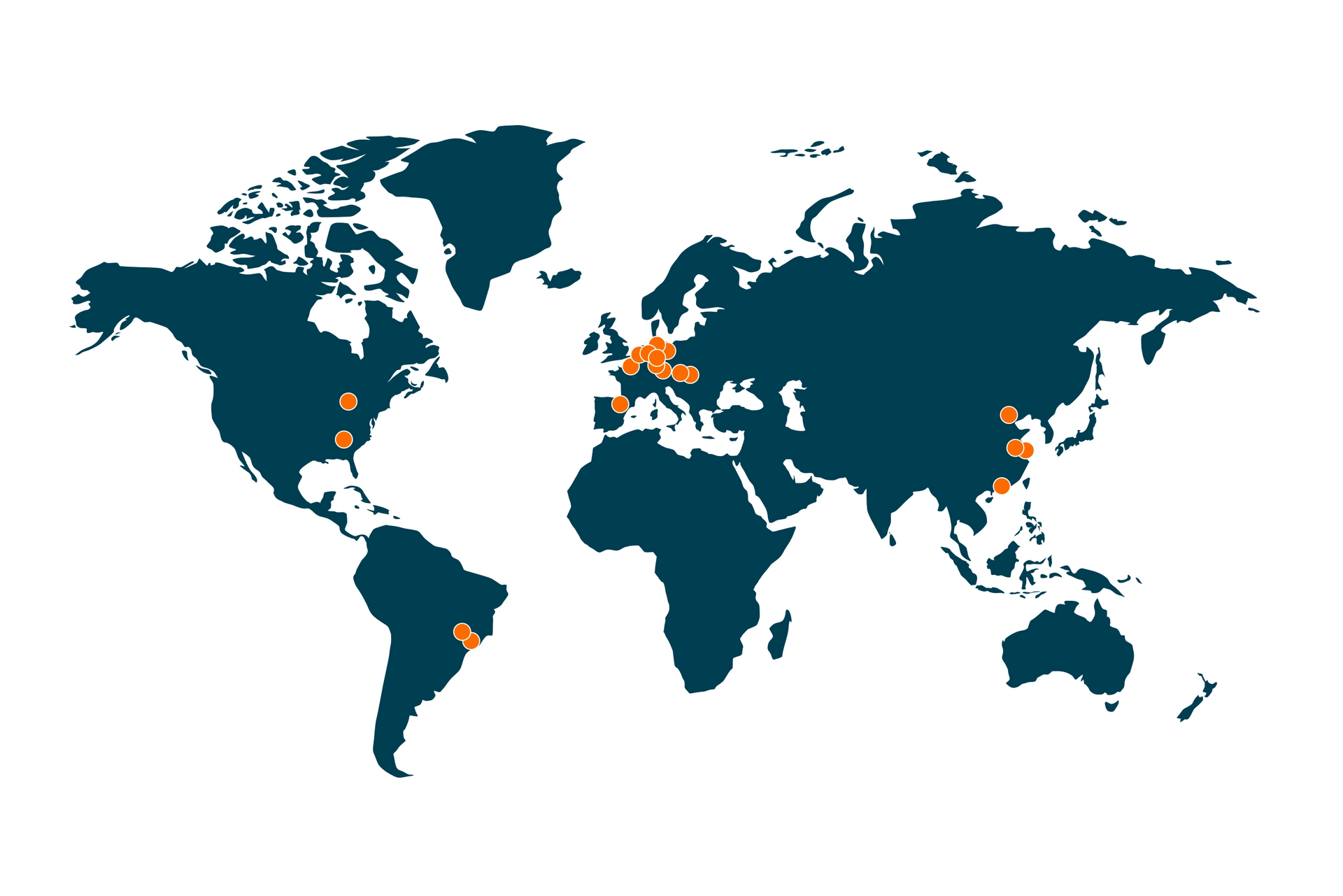
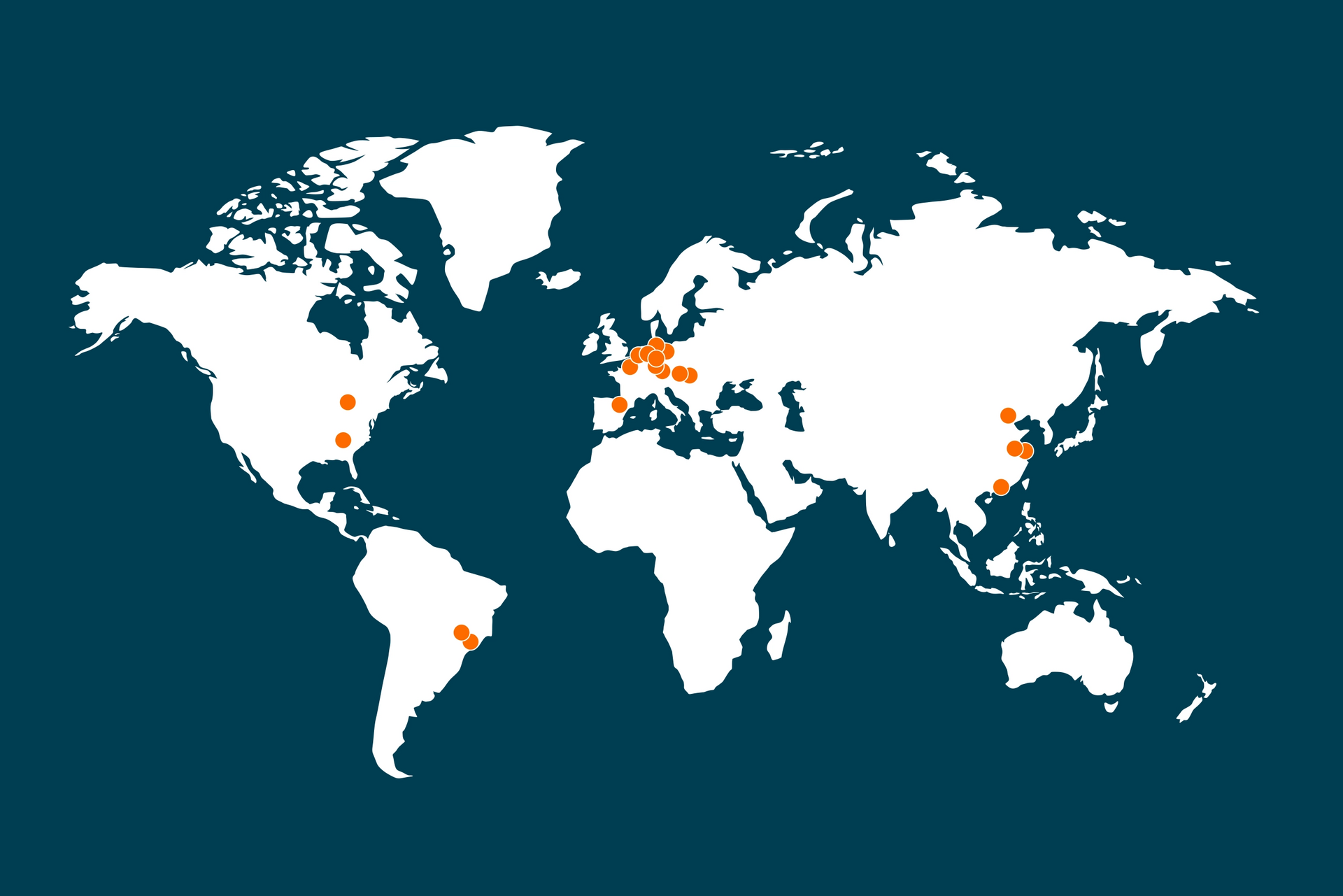
20+ locations globally
With offices in North and South America, Europe and China, we are where our customers are. Our footprint lets us work closely and hands-on with global supply chains.
Webinars
Events
Upcoming events
What's new?
ExploreReady to optimize your supply chain?
As an innovative partner, we collaborate with our customers to develop solutions for the future.